| Ecology and Behavior | ||||||||||
| Characteristics | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Similar Species | ||||||||||
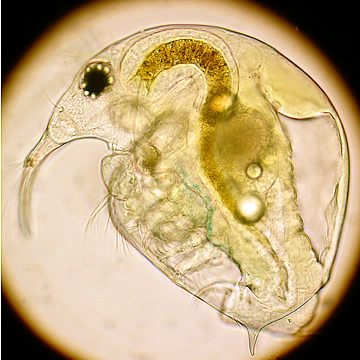
| Bosmina longirostris could be confused with Eubosmina longispina, which is distinguished by a sensory bristle near the tip of the rostrum, whereas B. longirostris has a sensory bristle midway between the eye and the tip of the rostrum. | ||||||||||
| Geographic Distribution | ||||||||||
| Bosmina longirostris is ubiquitous and occurs in temperate and tropical climates of Europe, Africa and the United States (2)(3). | ||||||||||
| Reported Habitats | ||||||||||
| B. longirostrisis normally found in the epilimnion (5) and in lakes with and without fish. (4). Commonly found in dystrophic or bog lakes (Haney, pers. comm.). | ||||||||||
| Food and Feeding Behavior | ||||||||||
| Despite their relatively small size of approximately 0.5 mm, B. longirostris are coarse filter-feeders, preferring large particles of 10-15 um, such as the diatom Cyclotella (?). Individuals fed low amounts of food will be smaller at maturity (6). | ||||||||||
| Reproductive Habits | ||||||||||
| Growth in B. longirostris continues after sexual maturity which allows older individuals to develop larger brood pouches and thus carry more eggs (6). Generally, adult Bosmina place most of their energy into reproduction and individuals at low food levels will develop fewer eggs than well fed animals (6). | ||||||||||
| Predation on Bosmina | ||||||||||
| B. longirostris is preyed on by visual predators, such as planktivorous fish, although it may benefit by its relatively small size, (3)(4). B. longirostris is also preyed upon by the invertebrate predator Chaoborus and cyclopoid copepods. In response to an attack, B. longirostris folds its swimming antennae under its antennules and passively sinks past these tactile predators; this “dead man” response continues until it is out of range (4). Other invertebrate predators of B. longirostris include: Mysis relicta, Leptodora kindtii, Epischura lacustris, Limnocalanus macrurus, Senecella calanoides, and cyclopoids (6). The pellucida antennule morph provides better protection against cyclopoid predation than the cornuta morph (9). Physical stimuli of attempted predations by cyclopoid copepods (9) and low water temperature (8) can induce antennule shape changes in B. longirostris, though predator kairamones alone had no effect (9). | ||||||||||
| Swimming Behavior | ||||||||||
| B. longirostris may form dense patches or swarms that exceed 9000 animals per liter when it is light and food is abundant (7). Such swarming behavior appearsto serve as protection against fish predation (7). Except for Polyphemus, Bosmina, like other cladocerans, does not swim in one continuous motion, but moves by a series of jumps caused by the motion of it's antennae (1). | ||||||||||
| References | ||||||||||
|
(1) KERFOOT, C. AND R. ZARET. 1980. The shape and swimming technique of Bosmina longirostris. Limnol. Oceanogr. 25: 126-133. (2) THRELKELD, S. 1981. The recolonization of Lake Tahoe by Bosmina longirostris: evaluating the importance of reduced Mysis relicta populations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 26: 433-444. (3) ZARET, T. AND C. KERFOOT. 1975. Fish predation on Bosmina longirostris: body-size selection versus visibility selection. Ecology. 56: 232-237. (4) VON ENDE, C. AND D. DEMPSEY. 1981. Apparent exclusion of the cladoceran Bosmina longirostris by invertebrate predator Chaoborus americanus. Am. Midl. Nat. 105: 240-248 (5) BLACK, R. 1980. The nature and cause of cyclomorphosis in a species of the Bosmina longirostirs complex. Ecology. 61: 1122-1132. (6) BRANSTRATOR, D. AND J. LEHMAN. 1991. Invertebrate predation in Lake Michigan: regulation of Bosmina longirostris by Leptodora kindtii. Limnol. Oceanogr. 36: 483-495. (7) JAKOBSEN, P. AND JOHNSEN, G. 1988. The influence of food limitation on swarming behaviour in the waterflea Bosmina longispina. Anim. Behav. 36: 991-995. (8) SAKAMOTO, M. AND HANAZATO, T. 2009. Proximate factors controlling the morphologic plasticity of Bosmina: linking artificial laboratory treatments and natural conditions. Hydrobiologia. 617: 171-179. (9) SAKAMOTO, M., K.H. CHANG, AND T. HANAZATO. 2007. Plastic phenotypes of antennule shape in Bosmina longirostris controlled by physical stimuli from predators. Limnol. Oceanogr. 52: 2072-2078. |
||||||||||
| Additional Pictures | ||||||||||
|
||||||||||
| Quicktime Movies | ||||||||||
|