|
|
||||
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
|
||||
Classification: |
||||
Vacuolaria Cienkowski 1870; 5 of 23 species descriptions are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry and Guiry 2013).Order Chattonellales; Family Vacuolariaceae |
||||
Morphology: |
||||
|
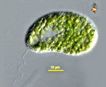
Motile cells with two flagella approximately as long as the cell itself. One flagellum is directed forward, the other ward. Cells have a convex dorsal surface and a flattened ventral surface. One to six contractile vacuoles. Vacuolaria is in the "green line" of raphids. Cell spherical to oblong or cylindrical, variable in size; many plastids with globular mucocysts. A stage of non-motile ‘palmelloid’ cells can form after a motile cell divides and secretes a thick mucilage coat (Pentecost 2011). |
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
Gonyostemum has ejectosomes (a.k.a. trichocysts) while Vacuolaria has muciliferous bodies that may represent rudimentary ejectsomes (Pentecost 2011). |
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
References: |
||||
|
Cienkowsky, L. 1870. Über Palmellaceen und einige Flagellaten. Arch. Mikroskop. Anat. 6: 421-438. Graham L. and Wilcox L. 2000. Algae. Prentice-Hal. Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 10 September 2013. Pentecost, A. 2011. Phylum Raphidophyta. In: The freshwater algal flora of the British Isles. John, D.M., B.A. Whitton and A.J. Brook (Eds.). (878 pp.) |
||||