|
|
||||
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
"Ball of bolts", from the Greek gomphos, a bolt, a club, and sphaira, a ball. |
||||
Classification: |
||||
|
Gomphosphaeria Kützing 1836; 12 of 31 species descriptions are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry and Guiry 2013). Order Chroococcales; Family Gomphosphaeriaceae |
||||
Morphology: |
||||
|
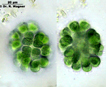
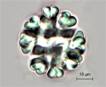
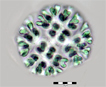
Spherical colonies of club-shaped cells, or heart-shapedwhen dividing, that are joined in the middle of the colony by a system of mucilaginous stalks that widen at the periphery of the colony to enclose individual cells.The colonies are within a mucilaginous envelope. |
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
Could be confused with the green algae Dictyosphaerium and Dimorphococcus, however those genera lack the mucilaginous envelope. |
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
Planktonic in lakes . The speciesG. aponina produces a substance termed aponin, and when grown in mixed culture with the red tide dinoflagellate Gymnodinium breve, appeared to be responsible for its lysis (McCoy and Martin 1977). |
||||
References: |
||||
|
Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 04 September 2013. Kützing, F.T. 1836. Algarum aquae dulcis germanicarum Decas XVI. pp. [1-25]. Halis Saxonum [Halle]: in commissis C.A. Schwetschkii et fil.. McCoy L. F. Jr. and D. F. Martin. 1977. The influence of Gomphosphaeria aponina on the growth of Gymnodinium breve and the effect of aponin on the ichthyotoxicity of Gymnodinium breve. Chemico-biological interactions 17(1): 17-24 |
||||