|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Colonies, Microcoleus or return to: |
||||
|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Filaments / Unbranched / Untapered / No Heterocysts / Visible Sheath |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
From the Greek Mikros –small, and koleos –sheath |
||||
Classification: |
||||
|
Microcoleus Desmazières ex Gomont 1892; 39 of 109 species descriptioins are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry and Guiry 20132). Order Oscillatoriales; Family Phormidiaceae
Synonym Chthonoblastus In PhycoKey you can find Microcoleus either has a colony or as a filament, because it forms a colony of more or less parallel filaments. |
||||
Morphology: |
||||
|
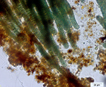
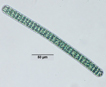
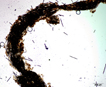
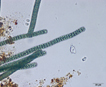
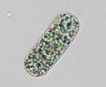
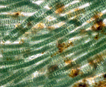
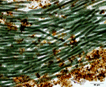
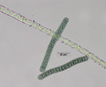
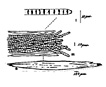
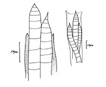
Colony of multiple trichomes within a common sheath, can be found either as a colonial or a filamentous cyanobacterium in PhycoKey. Unbranched and untapered trichomes lacking heterocysts, lying in a parallel array bounded by a common broad sheath. Individual trichomes are motile, sliding back and forth over one another. Microcoleus can be treated both filamentout (trichomes within a sheath and as colonial. In this key you can arrive at the Microcoleus genus page either way). Base sequences of 16S rRNA were identical or virtually identical from seven geographically widely separated natural populations of M. chthonoplastes at least to the genus level (Garcia-Pichel et al. 1996). |
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
Hydrocoleus trichomes also have low density sheaths, but few trichomes are contained within a common sheath, whereas Microcoleus sheath houses many trichomes. |
||||
Phototaxis: |
||||
Microcystis has +phototaxis (movement toward a light source) at low intensity, ≤ 17 µmol photons m-2 s-1) and –phototaxis at higher intensities (Garcia-Pichel et al. 1996). |
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
Benthic mats form in salt-marshes and marine lagoons, and in lakes, occasionally
1 m thick in hypersaline lakes (Jørgensen et al. 1986). Associations between colonies of Microcoleus with
macrophytes, especially the aquatic moss Fontinalis sp.,
and also Myriophyllum and Ceratophyllum, are common in lakes in the
vicinity of Berlin, Germany. Concentrations of anatoxins (1 to 9.2 mg g-1 fresh weight)
in these associations have resulted in numerous dog deaths. Much higher
levels of the toxin are found in associations with neustonic pine pollen (Pinus sylvestris) floating in lakewater, such
as Tegeler See (Fastner et al. 2023). An intriguing question is whether these
associations are strictly mechanical, or include metabolic exchange that
enhances cyanobacterial growth. Pine pollen degrades rapidly,
within hours releases >80% of contents including phosphorus that is ~0.3%
of biomass (3 mg g-1 P. sylvestris pollen), enabling uptake by
bacteria (Rösel
et al. 2012). Microcoleus would
greatly benefit, thus metabolic activity is likely. Colonies can also be terrestrial, as in sandstones and calcareous
soils in the Colorado Plateau (Utah, Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico USA) in
the upper 4 mm of soil, where they add stability minimizing erosion (Belnap
and Gardner 1993). |
||||
Nitrogen fixation at night: |
||||
|
Typical of non-heterocystous cyanobacteria, mats of Microcoleus chthonoplastes had high rates of N-fixation at night and little or none during the day (Omoregie et al. 2004), thus separating photosynthesis from respiration as source of energy for producing ammonia. |
||||
Alternating oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis |
||||
Microcoleus chthonoplastes can switch between oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis depending on the concentration of sulfide, and can conduct both types of photosynthesis simultaneously during the transition from one to the other. A lag period of 0 – 6 minutes from initiation of illumination to onset of oxygen release increases with sulfide concentration from 0 – 1000 µmol L-1 (Jørgensen et al. 1986). At 70 µmol L-1 rates of both oxygenic and anoxygenic photosynthesis were about equal (50:50). |
||||
Known toxins: |
||||
|
Microcystin and anatoxin. |
||||
References: |
||||
|
Belnap, J. and J.S. Gardner 1993. Soil microstructure in soils of the Colorado Plateau: The role of the cyanobacterium Microcoleus vaginatus. Great Basin Naturalist 53(1):40-47. Fastner, J., J. Teikari, A. Hoffman, A. Kohler, S. Hoppe, E. Dittmann, and M. Welker 2023. Cyanotoxins associated with macrophytes in Berlin (Germany) water bodies – Occurrence and risk assessment. Science of the Total Environment 858(1):1-11. Garcia-Pichel, F., L. Prufert-Bebout and G. Muyzer 1996. Phenotypic and phylogenetic analyses show Microcoleus chthonoplastes to be a cosmopolitan cyanobacterium. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 62(9):3284-3291. Gomont, M. 1892. Monographie des Oscillariées (Nostocacées homocystées).Annales
des Sciences Naturelles, Botanique,
Séries 7, 15:
263-368, pls 6-14 [VI-XIV in text and expl. pl.]. Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 04 September 2013. Jaeger E. C. 1972. A source-book of biological names and terms. 3rd Ed. Charles C. Thomas Publisher Jørgensen, B.B., Y. Cohen and N.P. Revsbech 1986. Transition from anoxygenic to oxygenic photosynthesis in a Microcoleus chthonoplastes cyanobacterial mat. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 51(2):408-417. Omoregie, E.O., L.L. Crumbliss, B.M. Bebout and J.P. Zehr 2004. Determination of nitrogen-fixing phylotypes in Lyngbya sp. and Microcoleus chthonoplastes cyanobacterial mats from Guerrero Negro, Baja California, Mexico. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 70(4):2119 – 2128. Rösel, S.; Rychła, A.; Wurzbacher, C.; Grossart, H.-P. Effects of pollen leaching and microbial degradation on organic carbon and nutrient availability in lake water. Aquat. Sci. 2012, 74, 87–99. Wehr J.D. and R. G. Sheath 2003. Freshwater Algae of North America. Academic Press (Imprint of Elsevier) Whitford L.A. and G.J. Schumacher 1973. A manual of fresh-water algae. Sparks Press |
||||
|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Colonies, Microcoleus or return to: |
||||
|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Filaments / Unbranched / Untapered / No Heterocysts / Visible Sheath |
||||