|
Home / Chrysophyceae / Unicells / Amoeboid / Chrysamoeba |
||||
|
|
||||
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
|
||||
Classification: |
||||
Chrysomoeba G.A. Klebs 1892; 3 of 4 species descriptions are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry and Guiry 2014).Order Chromulinales; Family Chrysamoebaceae
Probable synonym: Rhyzochrysis is described as only amoeboid and likely is part of the life cycle of Chrysamoeba (Hibberd 1971, Starmach 1985) |
||||
Morphology: |
||||
|
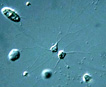
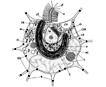
Golden amoeboid unicells during the majority of their life cycle with sometimes branched rhizopods, and one or two chloroplasts. At least some species are known to form silica stomatocysts (a resting stage). ). A flagellated stage that enables distribution but lasts a short time, eventually settles onto a surface such as a green filament and again becomes amoeboid (Hibberd 1971). |
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
|
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
Freshwater lakes and marine habitats. Widely distributed globally. |
||||
References: |
||||
|
Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2014. "'>AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 08 May 2014. Hibberd, D.J. 1971. Observations on the cytology and ultrastructure of Chrysamoeba radians Klebs *(Chrysophyceae). Brithish Phycological Journal 6(2):207-223. Klebs, G.A. (1893). Flagellatenstudien. Theil II. Zeitschrift für wissenschaftliche Zoologie 55: 352-445. Starmach, K. 1985. Chrysophyceae and Haptophyceae. In: Ettl, H., J. Gerloff, H. Heynig, and D. Mollenhauer, Eds. Susswasserflora von Mitteleuropa 5. Gustav Fischer, Stuttgart:1-515.
|
||||