|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Colonies / Aphanothece |
||||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
||
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
“Invisible box” (From the Greek, aphanes, invisible and theke, case or box) |
||||
Classification: |
||||
Aphanothece Nägeli 1849; 53 of 101 ‘species’ descriptions are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry 2013).Order Chroococcales; Family Chroococcaceae Synonym: Coccochloris K.P.J.Sprengel, 1807
|
||||
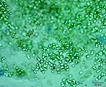
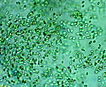
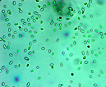
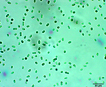
Morphology: |
||||
|
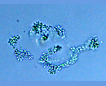
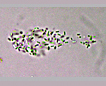
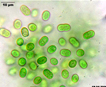
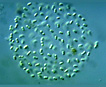
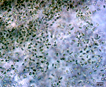
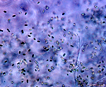
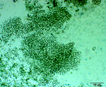
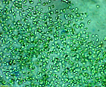
Many bacilliform (oblong), flattened cells unevenly distributed within mucilage, forming amorphous colonies. No distinct mucilage sheath around individual cells (cf. Gloeothece) |
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
Aphanocapsa can be distinguished from Aphanothece by the cells spherical shape. Gleothece cells are enclosed in a denser mucilage, cells individually surrounded by an envelope distinct from the larger mass of mucilage. |
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
Common in diverse environments. Planktonic or benthic in freshwater lakes and ponds, or coastal brackish habitats. Also on wet rock surfaces and soil. Along with Aphanocapsa and Entophysalis, Aphanothece species are the main sediment formers on marine coasts (Carr and Whitton 1973. |
||||
References: |
||||
|
Carr, N.G. and B.A. Whitton 1973. The biology of blue-green algae. University of California Press (676 pp). Guiry, M.D. and Guiry, G.M. 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 11 January 2013. John D. M., B. A. Whitton
and A. J. Brook, ed. 2008. Nägeli, C. 1849. Gattungen einzelliger Algen, physiologisch und systematisch bearbeitet. Neue Denkschriften der Allg. Schweizerischen Gesellschaft für die Gesammten Naturwissenschaften 10(7): i-viii, 1-139, pls I-VIII. Wehr J.D. and R. G. Sheath. 2003. Freshwater
Algae of |
||||