|
|
||||
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
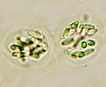
From the Greek rhabdos –a rod, and gloios- glutinous, gelatinous, sticky.
|
||||
Classification: |
||||
Dactylococcopsis Hansgirg 1888; 10 of 55 species descriptions are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry and Guiy 2013).Order Chroococcales; Family Chroococcaceae
|
||||
Morphology: |
||||
|
Colonies of fusiform cells without distinct sheath. D. salina forms gas vesicles (‘vacuoles’) (Walsby et al. 1983).
|
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
Rhabdogloea is a synonym. Geitler (1932) makes reference to Ankistrodesmus (eukaryotic colonial Chlorophyte) as sufficiently similar to be easily mistaken for Dactylococcopsis.
|
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
Most species are planktonic in lakes and reservoirs. Some are found within the mucilage of Microcystis colonies. |
||||
References: |
||||
|
Geitler, L. 1932. Cyanophyceae von Europa. Akademische Verlagsgesellschaft m. b. H. Leipzig (1,196 pp). Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 04 September 2013. Walsby, A.E., J. van Rihn and Y. Cohen. The biology of a new gas-vacuolate cyanobacterium, Dactylococcopsis salina sp.nov., in Solar Lake. Proceeding of the Royal Society of London B 217:417-447. |
||||