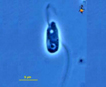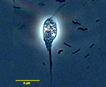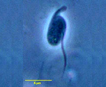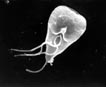


Flagellates are protists bearing few flagella, generally two (a pair). Some are photosynthetic (treated in phycokey within classes of “algae”), many others are heterotrophic. Their range of habitat is immense, both free-living and endobiotic.
Many are bacteriovores capable of rapid water clearance.
Most flagellates are in the size range of 5 – 20 mm.
Diseases caused by flagellates:
In humans and other mammals, several widespread diseases are caused by flagellates. Perhaps the most widespread is giardiasis caused by the intestinal parasite Giardia lamblia, with symptoms such as diarrhea (water and nutrient loss) and painful abdominal cramps.
African Sleeping Sickness is caused by Trypanosoma brucei, a parasite transmitted by tsetse flies (Glossina spp.), that has only one flagellum and swims in a corkscrew fashion (hence the name trypano-). The disease occurs in two stages – 1) haemolymphatic infection of blood and lymph systems; followed by 2) neurological invastion of the central nervous system (irreversible stages) which without medical treatment is ultimately fatal.
[Note: A group of non-flagelled, non-ciliated, and non-amoeboid protists – the Sporozoans – are also responsible for widespread human diseases such as malaria (Plasmodium sp., transmitted by mosquitoes) and toxoplasmosis (Toxoplasma gondii, contracted from unpasteurized milk, undercooked meat, or house cats) that causes serious fetal deformities in infected pregnant women. All sporozoans are parasites (not free-living) so are not included in phycokey.]
References:
Leadbeater, B.S.C., and J.C. Green (Eds.) 2000. The Flagellates – Unity, diversity and evolution. Taylor & Francis, London and New York, publishers.
Patterson, D.J. 1996. Free-Living Freshwater Protozoa. A Colour Guide. UNSW Press, Sydney.