|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Filaments / Unbranched / Tapered / Rivularia or return to: |
||||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Click on images for larger format |
||||
Name derivation: |
||||
|
|
||||
Classification: |
||||
|
Rivularia C.Agardh ex Bornet and Flahault 1886; 41 of 94 species descriptions are currently accepted taxonomically (Guiry and Guiry 2013). Order Nostocales; Family Rivulariaceae
|
||||
Morphology: |
||||
|
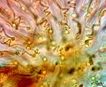
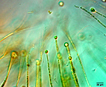
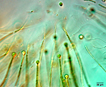
Tapered trichomes generally form a colony with trichomes radiating outward. Multi-layered colonies form, probably on an annual basis. A terminal heterocyst differentiates at the base of each filament. In PhycoKey Rivularia can be reached either through the filamentous or colonial lines because it is a colony of radiating filaments.
|
||||
Similar genera: |
||||
|
Gloeotrichia is planktonic and forms a morphologically similar colony of radiating, tapered filaments with basal heterocysts. |
||||
Habitat: |
||||
|
Freshwater and marine (Sihvonen et al. 2007), attached to various substrates |
||||
References: |
||||
|
Bornet, É. and C. Flahault 1886. Revision des Nostocacées hétérocystées contenues dans les principaux herbiers de France. Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Botanique, Septième série 3: 323-381. Guiry, M.D. and G.M. Guiry 2013. AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. http://www.algaebase.org; searched on 04 September 2013. Sihvonen, L.M., C. Lyra, D.P. Fewer, P. Rananiemi-Wacklin, J.M. Lehtimaki, M. Wahlsten and K. Sivonen 2007. Strains of the cyanobacterial genera Calothrix and Rivularia isolated from the Baltic Sea display cryptic diversity and are distantly related to Gloeotrichia and Tolypothrix. FEMS (Fereration of European Microbiological Societies) Microbiological Ecology 61:74-84. |
||||
|
Home / Cyanobacteria / Filaments / Unbranched / Tapered / Rivularia or return to: |
||||