|
|
||||
|
Click
on images for larger format |
||||
|
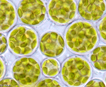
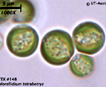
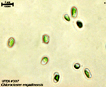
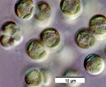
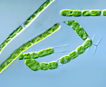
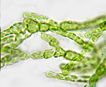
The class name
Tribophyceae has succeeded Xanthophyceae
to correspond to type genus Tribonema, instead of xantho-,
color yellow (Hibberd 1981, Christensen 1987). Previously the few known taxa were placed
in the Chlorophyceae because of their frequently green color.
The class Tribophyceae
currently includes ~ 100 genera and 600 species (Johnson 2011). They contain chlorophylls a and small amounts of c1 and c2 in discoid
chloroplasts. The principal accessory
pigments include the blue-absorbing yellow pigments B-carotene,
vaucheriaxanthin, diadinoxanthin, and heteroxanthin
(van den Hoek et al. 1995). As members of the heterokonts –
protists with two dissimilar flagella – the Tribophyceae
produce the polysaccharide chrysolaminaran (but not
starch), soluble in aqueous solution, and stored in vacuoles.
Tyge Christensen Tyge Ahrengot Christensen (1918 - 1996) was
a Danish botanist who was an associate professor at the University of
Copenhagen and received an honorary doctorate there in 1986. In 1962, he wrote 'Algae - a taxonomic survey', a textbook on the systematics and biology of algae. His research focused on the
yellow-green algal genus Vaucheria. He was one of
the initiators of the establishment of The International Phycological Society
and co-editor of Phycologia (1961-69) as well as a
member of the International Nomenclature Committee for Algae (1959-87). He was also editor of 'Seaweeds of the British Isles. Volume 4 (Christensen 1987).
Christensen was also a member of the Natural
Science Committee of the Danish Nature Conservation Association (1956-64) and
of the Nature Conservation Council (1973-77). In his memory, the
International Phycological Society has established The Tyge Christensen
Prize, which is awarded every two years. The prize of 5000 dollars is given
for the best scientific article on algae published in the society's journal
in the previous two years. |
||||
|
References: |
||||
|
Christensen,
T. 1987. Seaweeds of the British Isles. Volume 4 Tribophyceae (Xanthophyceae).
British Museum (Natural History), London ISBN 0-565-00980-X Johnson,
L. 2011. Phylum Xanthophyta
(Tribophyta)(Yellow-Green Algae). In: The
Freshwater Algal Flora of the British Isles, 2nd edition. John, D.M., B.A.
Whitton, and A.J. Brook, Eds. (878 pp). van den Hoek, C., D.G. Mann, and H.M. Jahns 1995.
Algae – An Introduction to Phycology.
Cambridge University Press (623
pp.) . |
||||